The Accounting Equation

The Accounting Equation

If we rearrange the Accounting Equation, Equity is equal to Assets minus Liabilities. Net Assets is the term used to describe Assets minus Liabilities. You can think of them as resources that a business controls due to past transactions or events. Understanding how the accounting equation works is one of the most important accounting skills for beginners because everything we do in accounting is somehow connected to it. Suppose a proprietor company has a liability of $1500, and owner equity is $2000. Calculation of Balance sheet, i.e., Total asset of a company will sum of liability and equity.
The Accounting Equation
This transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation; both the left and right sides of the equation increase by +$250. This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation. The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value.
- Parts 2 – 6 illustrate transactions involving a sole proprietorship.Parts 7 – 10 illustrate almost identical transactions as they would take place in a corporation.Click here to skip to Part 7.
- As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets.
- The cash (asset) of the business will increase by $5,000 as will the amount representing the investment from Anushka as the owner of the business (capital).
- The accounting equation relies on a double-entry accounting system.
The Financial Modeling Certification
Parts 2 – 6 illustrate transactions involving a sole proprietorship.Parts 7 – 10 illustrate almost identical transactions as they would take place in a corporation.Click here to skip to Part 7. Metro Corporation collected a total of $5,000 on account from clients who owned money for services previously billed. Metro issued a check to Office Lux for $300 previously purchased supplies on account.
What Are the 3 Elements of the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. EIOPA’s backward and forward-looking analysis of equity and spread risks demonstrates that fossil fuel-related stocks and bonds are more exposed to transition risks than assets connected to other economic activities. To ensure that European insurers set aside enough capital to withstand potential losses from investments in assets with high transition risks, EIOPA is recommending additional capital charges for these assets.
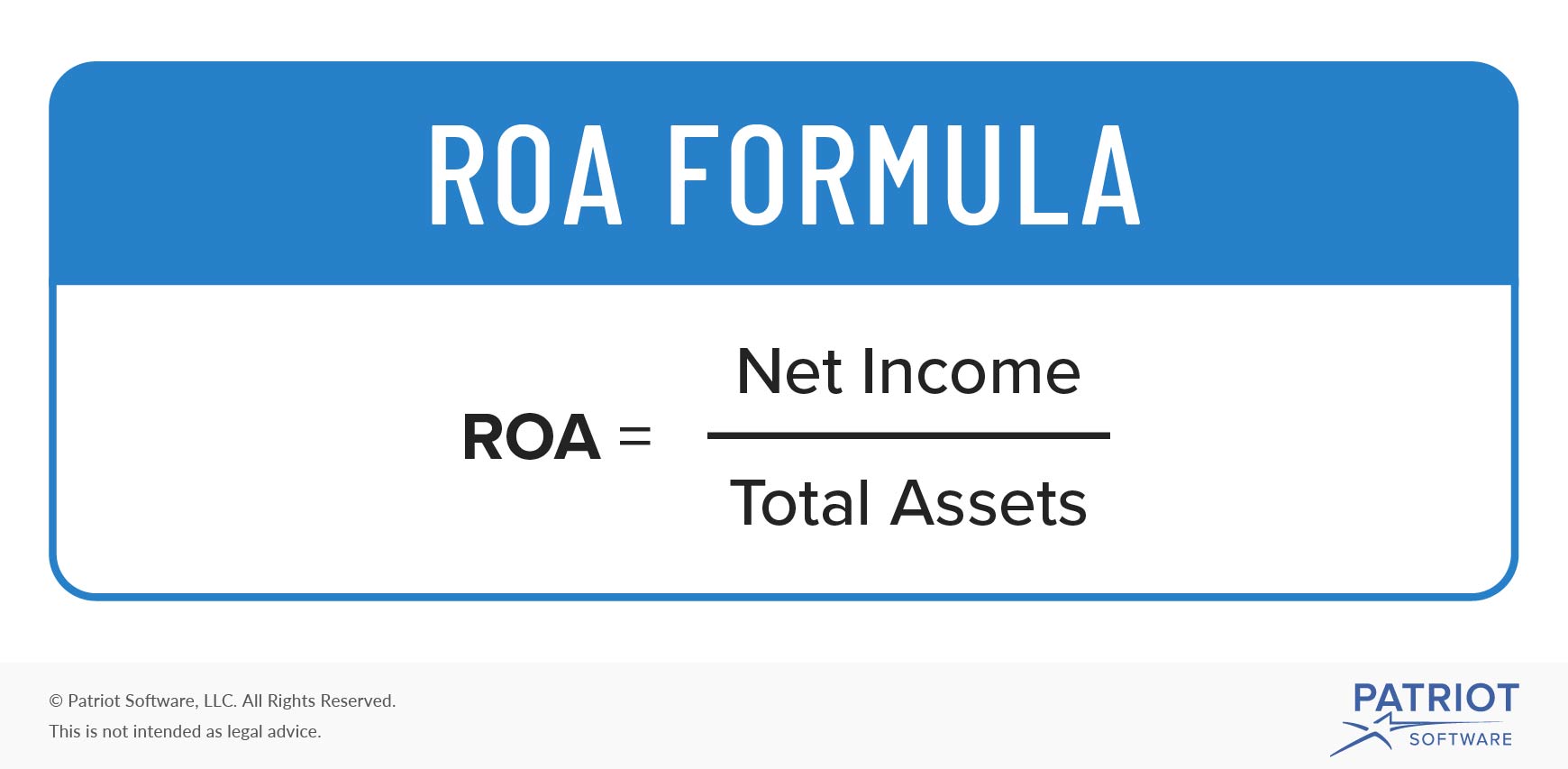
Before explaining what this means and why the accounting equation should always balance, let’s review the meaning of the terms assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity. The asset equals the sum of all assets, i.e., cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expense, and inventory, i.e., $234,762 for 2014. The asset equals the sum to all assets, i.e., cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expense, and inventory, i.e., $305,483 for the year 2018. As transactions occur within a business, the amounts of assets, liabilities, and owner's equity change.
Assets, Liabilities, And Equity
The accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity. This shows all company assets are acquired by either debt or equity financing. For example, when a company is started, its assets are first purchased with either cash the company received from loans or cash the company received from investors. Thus, all of the company’s assets stem from either creditors or investors i.e. liabilities and equity. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets.
From the accounting equation, we see that the amount of assets must equal the combined amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity. You can find a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity on key financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements (also called profit and loss statements). These financial documents give overviews of the company’s financial position at a given point in time.
Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. Owner’s or stockholders’ equity also reports the amounts invested into the company by the owners plus the cumulative net income of the company that has not been withdrawn or distributed to the owners.
An error in transaction analysis could result in incorrect financial statements. An accounting transaction is a business activity or event that causes a measurable change in the accounting equation. Merely placing an order for goods is not a recordable transaction because no exchange has taken place. In the coming sections, you will learn more about the different kinds of financial statements accountants generate for businesses. Assets entail probable future economic benefits to the owner. As you can see, assets equal the sum of liabilities and owner’s equity.
The major and often largest value assets of most companies are that company’s machinery, buildings, and property. These are fixed assets that are usually held for many years. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or retail sales and use tax liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs). The Commission will review the report and consider implementing the proposed additional capital requirements for fossil fuel assets.
As a result of this transaction, an asset (i.e., cash) increases by $10,000 while another asset ( i.e., merchandise) decreases by $9,000 (the original cost). On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created. At this time, there is external equity or liability in Sam Enterprise.
